What is APQC Process Analysis?
APQC Process Analysis is a structured method for understanding, mapping, and improving business processes.
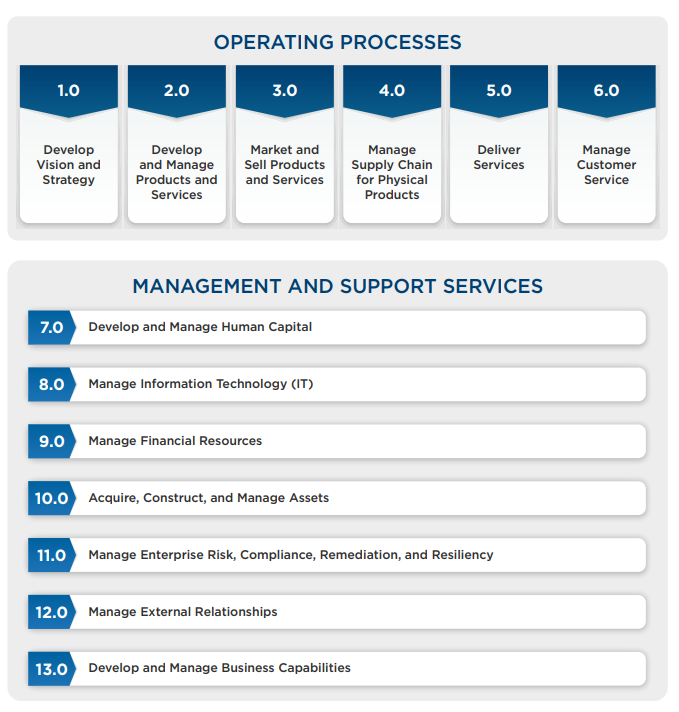
It uses the APQC Process Classification Framework (PCF), a global standard for process categorisation.
The framework offers a consistent language so businesses can compare, benchmark, and enhance their operations.
Rather than focusing on just documentation, APQC Process Analysis looks at the bigger picture — how work is completed and where value is created or lost.
How to Use APQC Process Analysis
Start by identifying the processes you want to assess.
Use the PCF to classify them, ensuring consistency and clarity across the business.
Break each process into smaller components, documenting the steps, inputs, outputs, and responsible roles.
Involve the people who do the work daily — they know the practical realities, not just the theory.
Once mapped, review each step to find inefficiencies, bottlenecks, or redundancies.
Use measurable data like time taken, error rates, or customer satisfaction to back up your findings.
From there, design an improved “to-be” process and communicate the changes clearly to your team.
Why APQC Process Analysis Matters
It provides a clear view of how your business runs, which is essential for improvement.
When processes are visible, they’re easier to measure, train, and optimise.
It aligns teams by creating a single reference point for how work should be done.
This approach reduces wasted effort, supports compliance, and improves consistency.
It also prepares the groundwork for automation — a process needs to be clearly mapped before it can be effectively automated.
Benchmarking and Best Practices
One of APQC’s strengths is its benchmarking capability.
You can compare your processes against industry standards to identify strengths and weaknesses.
This insight shows where you’re leading the market and where you’re falling behind.
Benchmarking also makes goal-setting easier because you can base targets on proven standards.
Scalability and Change Management
Standardised processes make it easier to scale operations without losing quality.
As teams grow, clear documentation ensures new staff can get up to speed quickly.
It also supports change management — when employees see a documented process, they better understand the reasons behind adjustments.
Continuous Improvement
APQC Process Analysis isn’t a one-time project.
It works best as a continuous improvement cycle.
Regularly revisit your processes, measure results, and adjust based on new data or business needs.
This keeps operations efficient and adaptable in changing markets.
Real-World Examples
A manufacturing company might use APQC Process Analysis to streamline supply chain steps from supplier orders to delivery.
They might find an approval step that adds days to production, which could be automated or removed.
In a service-based business, mapping client onboarding ensures each client has a consistent experience.
This makes it easier to train staff and maintain quality at scale.
Final Thoughts
APQC Process Analysis is flexible enough to work across industries while providing a consistent structure.
It’s not about fitting every business into the same mould but about giving them the tools to improve how they operate.
With clear processes, businesses can respond faster to changes, operate more efficiently, and scale sustainably.